What the Canadian Federal Budget did for housing
Michael Hallett • March 28, 2019

Federal Budget 2019--Actions for Homebuyers
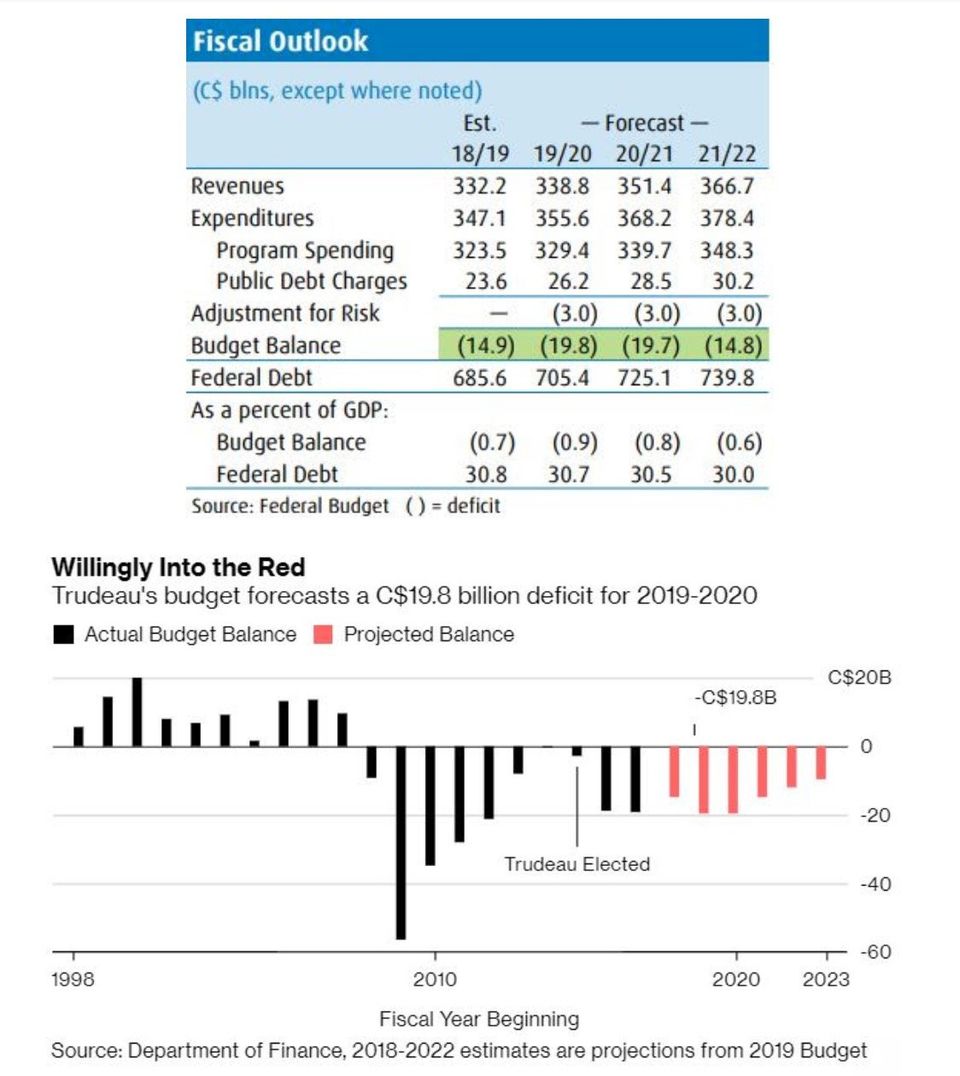
In its fourth fiscal plan, the Trudeau government spent its entire revenue windfall leaving the deficit projection little changed. In this election budget, Finance Minister Bill Morneau announced $22.8 billion over six years in new spending initiative mostly for homebuyers, students and seniors. Trudeau promised in his first budget to have eliminated all red ink by this year. He will instead head for an October election with an annual deficit of nearly $20 billion. Ottawa is projecting a string of double-digit deficits through the end of 2022 (see Table and Chart below).
The key debt-to-GDP ratio is expected to be 30.8% this fiscal year and edges downward only very slowly to 30% over the four-year forecast horizon.
Today's budget offered help to young homebuyers, many of whom find it very difficult to afford to purchase in some of our more expensive cities. There were two measures targeted at first-time homebuyers:
Maximum Withdrawal from RRSPs Is Increased
The simplest to understand is the $10,000 increase in the federal Home Buyers' Plan (HBP)maximum tax-free withdrawal from RRSPs to $35,000, effective immediately. This allowable withdrawal for first-time buyers will now also apply to people experiencing the breakdown of a marriage or common-law partnership who don't meet the usual requirement of being a first-time homebuyer.
The new limit would apply to HBP withdrawals made after March 19, 2019.
Those taking advantage of the higher HBP limit will have to keep in mind that the repayment timeline is unchanged. Home buyers must put the money back into their RRSP over 15 years to avoid full ordinary income taxation on HBP withdrawal. Now Canadians using these funds will have to repay a maximum of $35,000 – instead of $25,000 – over the same period.
The Boldest Move: The CMHC First-Time Homebuyer Incentive
A $1.25 billion fund administered by the Canadian Mortgage and Housing Corporation (CMHC) over three years will provide 5% of the cost of an existing home and 10% of the price of a new home through what amounts to an interest-free loan to be repaid when the property is sold. The money would go to first-time home buyers applying for insured mortgages. The key stipulations are:
- Users must have a downpayment of at least 5%, but less than 20%;
- Household income must be less than $120,000;
- The purchase price cannot be more than four times the buyers' household income.
For example, say you’re hoping to buy a $400,000 home with the minimum required 5% down payment, which works out to be $20,000. With the new incentive, you could receive up to $40,000 (for a new home) through the CMHC. Now, instead of taking out a $380,000 mortgage, you’d need to borrow only $340,000. This would lower your monthly mortgage bill from over $1,970 to less than $1,750. The incentive is 10% for buyers purchasing a newly built home and 5% for existing homes.
Homeowners would eventually have to repay this so-called 'shared mortgage,' likely at resale, though it is unclear how this would work. CMHC might share in any capital gain (or loss)-- receiving 5% or 10% of the sale price (not the purchase price). At the time of this writing, these details had not been hammered out.
These stipulations effectively limit purchases under this plan to properties priced at less than $500,000 ($480,000 maximum in insured mortgage and incentive, plus the downpayment), which is close to the national average sales price of $468,350 (which is down 5.2% from the average price one year ago). However, the national average price is heavily skewed by sales in Greater Vancouver and the Greater Toronto Area, two of Canada's most active and expensive markets. Excluding these two markets from the calculations cuts close to $100,000 off the national average price, trimming it to just under $371,000. What this tells us is that the relief for first-time homebuyers is pretty meagre for young people living in our two most expensive regions.
Arguably, the max price point of $500,000 for this plan is where the affordability challenge only really begins in our higher-priced housing markets. The most acute affordability problems surround medium-sized and larger condo units or single-detached homes in the GTA and GVA; yet, most of these are beyond the price range covered by the CMHC plan. The impact, of course, would be broader in other regions, but affordability in many of those is historically quite normal. The most significant impact will be in low-priced new builds.
Also, mortgage applicants under this plan still have to qualify under the federal stress test, which ensures that borrowers will be able to keep up with the payments even if interest rates rise by roughly two full percentage. The incentive, however, would substantially lower the bar for test takers, as applicants would have to qualify for a lower mortgage.
Before the budget, many stakeholders had been arguing that with the rapid slowdown in the economy and the Bank of Canada unlikely to raise interest rates this year, the B-20 stress test is too onerous and should be eased.
The government is hoping to have the plan up and running by September.
Bottom Line: These housing measures are focussed on the demand side of the market, rather than encouraging the construction of new affordable housing. And while the budget does earmark $10 billion over nine years for new rental homes, it does not propose tax breaks or reduced red tape for homebuilders.
This article was written by Dr. Sherry Cooper DLC's Chief Economist.
SHARE
MY INSTAGRAM
Mortgage Brokering meets mountain biking and craft beer. A couple months ago I set for a bike ride with the intention of answering few mortgage related questions, mission accomplished. Any good bike ride pairs nicely with a tasty beer which we enjoyed @parksidebrewery. Hope you see the passion I have for brokering, biking and beer. @torcabikes #mountainbikingmortgagebroker
TEASER alert...at thats what I think they call it in the business. Years ago a wrote a blog called BEERS BIKES AND MORTGAGES. I some how (in my head) blended all 3 topics into 1 blog. Simply put, I enjoy aspects of all 3 with each of them providing something different. I re-united with the talented Regan Payne on a project that I think will shed a bit more light on who I am and what I do. #craftbeer #mountainbike #mortgagebrokerbc #dlccanadainc
I saw this hat on Instagram, that very moment I knew I needed it. As a BC boy born and bred The Outdoorsman hat needed to be added to my collection. As someone who loves BC and most things outdoor, I’m now glad I have a cool hat to wear and fly the flag of BEAUTIFUL BRITISH COLUMBIA. It will be in my bag for all post-exploration celebratory cold pints. If you want to check them out or add one to your collection go to @nineoclockgun ...and yes my facial hair matches the hat as well.
View more

Bank of Canada maintains policy rate at 2¼%. FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE Media Relations Ottawa, Ontario January 28, 2026 The Bank of Canada today held its target for the overnight rate at 2.25%, with the Bank Rate at 2.5% and the deposit rate at 2.20%. The outlook for the global and Canadian economies is little changed relative to the projection in the October Monetary Policy Report (MPR). However, the outlook is vulnerable to unpredictable US trade policies and geopolitical risks. Economic growth in the United States continues to outpace expectations and is projected to remain solid, driven by AI-related investment and consumer spending. Tariffs are pushing up US inflation, although their effect is expected to fade gradually later this year. In the euro area, growth has been supported by activity in service sectors and will get additional support from fiscal policy. China’s GDP growth is expected to slow gradually, as weakening domestic demand offsets strength in exports. Overall, the Bank expects global growth to average about 3% over the projection horizon. Global financial conditions have remained accommodative overall. Recent weakness in the US dollar has pushed the Canadian dollar above 72 cents, roughly where it had been since the October MPR. Oil prices have been fluctuating in response to geopolitical events and, going forward, are assumed to be slightly below the levels in the October report. US trade restrictions and uncertainty continue to disrupt growth in Canada. After a strong third quarter, GDP growth in the fourth quarter likely stalled. Exports continue to be buffeted by US tariffs, while domestic demand appears to be picking up. Employment has risen in recent months. Still, the unemployment rate remains elevated at 6.8% and relatively few businesses say they plan to hire more workers. Economic growth is projected to be modest in the near term as population growth slows and Canada adjusts to US protectionism. In the projection, consumer spending holds up and business investment strengthens gradually, with fiscal policy providing some support. The Bank projects growth of 1.1% in 2026 and 1.5% in 2027, broadly in line with the October projection. A key source of uncertainty is the upcoming review of the Canada-US-Mexico Agreement. CPI inflation picked up in December to 2.4%, boosted by base-year effects linked to last winter’s GST/HST holiday. Excluding the effect of changes in taxes, inflation has been slowing since September. The Bank’s preferred measures of core inflation have eased from 3% in October to around 2½% in December. Inflation was 2.1% in 2025 and the Bank expects inflation to stay close to the 2% target over the projection period, with trade-related cost pressures offset by excess supply. Monetary policy is focused on keeping inflation close to the 2% target while helping the economy through this period of structural adjustment. Governing Council judges the current policy rate remains appropriate, conditional on the economy evolving broadly in line with the outlook we published today. However, uncertainty is heightened and we are monitoring risks closely. If the outlook changes, we are prepared to respond. The Bank is committed to ensuring that Canadians continue to have confidence in price stability through this period of global upheaval. Information note The next scheduled date for announcing the overnight rate target is March 18, 2026. The Bank’s next MPR will be released on April 29, 2026. Read the January 28th, 2026 Monetary Report

Mortgage Registration 101: What You Need to Know About Standard vs. Collateral Charges When you’re setting up a mortgage, it’s easy to focus on the rate and monthly payment—but what about how your mortgage is registered? Most borrowers don’t realize this, but there are two common ways your lender can register your mortgage: as a standard charge or a collateral charge . And that choice can affect your flexibility, future borrowing power, and even your ability to switch lenders. Let’s break down what each option means—without the legal jargon. What Is a Standard Charge Mortgage? Think of this as the “traditional” mortgage. With a standard charge, your lender registers exactly what you’ve borrowed on the property title. Nothing more. Nothing hidden. Just the principal amount of your mortgage. Here’s why that matters: When your mortgage term is up, you can usually switch to another lender easily —often without legal fees, as long as your terms stay the same. If you want to borrow more money down the line (for example, for renovations or debt consolidation), you’ll need to requalify and break your current mortgage , which can come with penalties and legal costs. It’s straightforward, transparent, and offers more freedom to shop around at renewal time. What Is a Collateral Charge Mortgage? This is a more flexible—but also more complex—type of mortgage registration. Instead of registering just the amount you borrow, a collateral charge mortgage registers for a higher amount , often up to 100%–125% of your home’s value . Why? To allow you to borrow additional funds in the future without redoing your mortgage. Here’s the upside: If your home’s value goes up or you need access to funds, a collateral charge mortgage may let you re-borrow more easily (if you qualify). It can bundle other credit products—like a line of credit or personal loan—into one master agreement. But there are trade-offs: You can’t switch lenders at renewal without hiring a lawyer and paying legal fees to discharge the mortgage. It may limit your ability to get a second mortgage with another lender because the original lender is registered for a higher amount than you actually owe. Which One Should You Choose? The answer depends on what matters more to you: flexibility in future borrowing , or freedom to shop around for better rates at renewal. Why Talk to a Mortgage Broker? This kind of decision shouldn’t be made by default—or by what a single lender offers. An independent mortgage professional can help you: Understand how your mortgage is registered (most people never ask!) Compare lenders that offer both options Make sure your mortgage aligns with your future goals—not just today’s needs We look at your full financial picture and explain the fine print so you can move forward with confidence—not surprises. Have questions? Let’s talk. Whether you’re renewing, refinancing, or buying for the first time, I’m here to help you make smart, informed choices about your mortgage. No pressure—just answers.